5 Key Areas to Enhance the SAP Knowledge
Category: SAP Posted:Aug 27, 2018 By: Ashley MorrisonThe market for Enterprise Resource Management (ERM) systems is currently dominated by one key player – SAP. This means that it is imperative for a prospective employee to enhance knowledge of SAP to facilitate higher productivity. ERM manages all data from every department in an organization ranging from office supplies to sensitive client information.
Source:c1.staticflickr.com
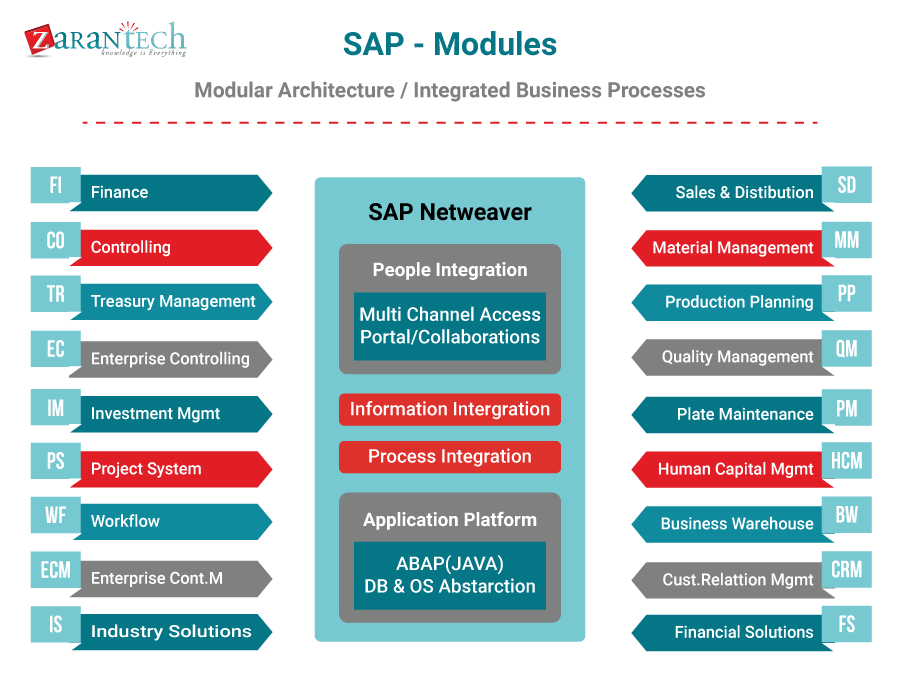
SAP has five main areas that an individual will be required to work within the position of a consultant. It is critical to comprehend the various sections of SAP for success at the workplace.
Get More Insights about SAP FICO with Live Webinar
1) SAP FI (Finance) and 2) SAP CO (Controlling):
The modules mentioned above are frequently called SAP FICO. This is because more often than not Financial Accounting requires features of control systems to manage profits and costs. SAP FICO is a chief functional part of SAP ERP Central Component which permits an enterprise to handle every part of its financial data sets. The sole objective of SAP FICO is to aid enterprises in the generation and management of financial statements for reporting and analysis. It also supports effective decision-making and Enterprise planning.
SAP FI handles all-inclusive financial reporting and accounting while SAP CO focuses on planning and cost monitoring. The reason most individuals refer to FI and CO as one module is because they are closely integrated with each other.
SAP FI modules:
With the help of an SAP FI module, the enterprises are able to create financial statements such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets which are utilized for reporting and analysis. SAP FI includes various sub-modules that manage particular accounting processes.
General Ledger includes the entire data sets comprising the enterprise’s transactional data through a chart of accounts that enlists all accounts present in the system.
All transactions are stored within sub-modules that can be reconciled with the general ledger data in real-time.
- Accounts Receivable records customer transactions and manages customer accounts. Transactions include invoice posting, down payments, dunning, credit memo posting, invoice payments, and executing customer reports.
- Asset Accounting manages the comprehensive set of transactions associated with the company’s fixed assets, including heavy equipment, buildings, and land. Transactions include sales, revaluations, asset acquisitions, depreciation, retirement, and transfers.
- Accounts Payable includes a comprehensive set of transactions with vendors and manages vendor accounts. Transactions involve invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, invoice payments, automatic payment program, and executing vendor reports.
- Bank Ledger deals with all of the company’s bank account data and transactions. It can reconcile all transactions recorded on bank statements and compare them with the transactions in the system.
- Special Purpose Ledger specifies the ledgers in SAP FI for purposes of reporting.
- Consolidation allows the enterprise to consolidate financial statements for multiple entities, which offers an overview of the company’s financial standing as a consolidated and single entity.
- Travel Management is responsible for managing all transactions for travel procedures, including those of booking trips and management of travel-related expenses.
- Funds Management oversees the budgets for the enterprise’s revenues and expenses.
SAP CO modules:
While SAP FI oversees Enterprise reporting both internal and external and accounting within the company, SAP CO aids the required processes to plan, report, and even monitor costs from enterprise operations. SAP CO you can be the deciding factor in enhancing business profitability. Similar to SAP FI SAP CO also consist of a sub-module that manages particular processes as given below:
- Cost Elements offers an overview of all the company’s costs and revenues founded on profit and loss statements, and these are also known as income statements. Cost element accounting defines the source of the costs, and the cost elements signify the precise costs that the business sustains.
- Cost Centers deal with the costs associated with the company’s internal divisions or departments, such as sales, production, marketing or human resources. Cost Centers only involve expenses, but not revenues.
- Profit Centers handle all of the cost data related to the company’s business lines. It deals with both expenses and revenues, unlike Cost Centers, which deals only with expenses. For example, a global consumer products company may use Profit Centers for health products, soaps and detergents, cosmetics, food and beverages, and so on.
- Profitability Analysis allows the enterprise to evaluate the profitability of its products. For example, Profitability Analysis can be beneficial for making decisions on matters like target market segments, distribution channels, or product pricing. It also permits levels of detail in evaluating profitability, such as for each region or country, product types, and distribution channels, down to individual customer profitability.
- Internal Orders are used to manage the costs for smaller internal projects or non-fixed assets, for example, a restricted or contingency based marketing campaign.
- Product costing manages the data about costs necessary to yield the company’s goods and services. Product costing analysis can help manage manufacturing costs and enhance efficiencies.
3) SAP SD (Sales and Distribution):
SAP SD is part of SAP ECC’s Logistics function and integrates with other modules, including Human Resources (HR), Materials Management (MM), Plant Maintenance (PM), Quality Management (QM), Finance and Controlling (FICO), and Production Planning (PP).
SAP Sales and distribution allows for an order-to-cash cycle enterprise process while working hand in hand with other modules in SAP. The sales and distribution module also manages all the specific sales and distribution end of the cycle. In an ideal cycle sales and distribution produce a sales quote followed by the customer placing a sales order. The next step involves the goods being sourced from the production facility or warehouse and shipped to the respective customer. Following this, an invoice is raised and dispatched in the order and the accounts receivable will settle the payment with the respective customer. Every step in this process will create transactions in the sales and distribution module which will create further transactions in the other existing ECC modules. For instance, when a sales order is created in sales and distribution it creates a link for product availability check to Materials Management and a Credit check to FICO or a tax calculation FICO.
Data types in SAP SD:
Just like every other module in SAP ECC, everything in SAP sales and distribution is contingent upon master data that is recorded and modified in centralized Master Data tables. There are also two other data types in ECC – they are customizing data and transactional data. The types of Master Data in sales and distribution include materials, pricing, and customer data. Master Data is utilized to generate transaction data in SAP ECC like a sales order in sales and distribution, purchase order in MM, maintenance record in PM, or production order in PP. Customizing data is created when a company customizes SD to meet its distinct needs.
SAP SD sub-modules:
SAP SD consists of several sub-modules that can be configured to handle specific functions in the module:
- SD Master Data (SD-MD) tracks every transaction that touches the SD module’s data, comprising credit management, materials data, customer data, and price condition records.
- SD Basic Functions (SD-BF) permits you to institute the elementary functions that work across SD, such as pricing, goods availability check, and credit management.
- SD shipping (SD-SHP) tracks the essential information related to the shipping process, which also involves the details of the order, i.e. how and when the order is shipped through to delivery or return.
- SD Sales Support (SD-CAS) handles the data produced in the interactions between sales teams and customers.
- SD Transportation (SD-TBA) works closely with the SD-SHP and keeps track of all the transportation data involved in the shipment.
- SD Sales (SD-SLS) handles the details of the sales process, such as products, customer data, feedback, and pricing.
- SD Foreign Trade (SD-FTT) handles the details related to foreign trade transactions, including both exports and imports.
- SD Billing (SD-BIL) manages billing data, including the amounts of the transactions and methods of payment.
4) SAP HR (Human Resources) and SAP Human Capital Management (HCM):
Consultants are not much interested in using this software, because the HR department of the organization will be dealing with payrolls, etc. However, the other features such as time organization management may be useful to have a fundamental knowledge of this software.
The objective of human resource management is to allow Enterprises to process employee data according to current business needs using effective structures. Inside the human resources module, makes use of data sets which are named Infotypes. Infotypes reflect a number of interconnected data records and are recognizable using a numerical string of four characters. [E.g. Infotype Addresses (0005)]. It is significant to mention a comprehensive listing included in this. One can save the info types as time-dependent to allow a retroactive analysis of Employee data. The Infotypes will be seen as an entry screen for the user, through which you can regulate Infotype records. info types can be processed individually or in a fast entry mode.
The SAP Human Capital Management (HCM) contains all the processes which are classified into two major scenarios, i.e. Workforce process management and talent management.
Workforce Process Management includes the following processes:
- Personnel time management and evaluation
- Organizational Management
- Employee administration
- Payroll calculation
- Benefits management
Talent Management includes the following processes:
- Employee performance management
- Compensation management
- Succession management
- Career management
- Enterprise Learning
- Recruiting
5) SAP PS (Project Systems):
The SAP project system is a project management software tool that integrates with pre-existing elements of the SAP enterprise resource planning system. This is a functional module that is on-premise and a component of the SAP ERP system which enables users to funnel resources and funds where it is required and monitor and direct each level of the project to make sure delivery happens within the specified time and budget.
The SAP project system allows users, including project managers to find a well-defined date for the start and end times of the project. It will also help project managers to split the allotted start and end dates into well-defined Structures and elements. Projects are organized using structures which in turn utilizes a work breakdown which allows segregation of the main project into the smaller individual tasks and also arranging them using a hierarchy structure and listing them accordingly. The project is also segregated using processes, and work packages which in turn make a list of activities and their aspects such as dates for starting and ending. Along with this, there is a network function that permits activities and their relationships to be determined.
SAP project systems are designed to be closely integrated with other SAP elements and can be utilized for projects of the entire spectrum of complexity and scope. It is worth noting that its features are best suited for projects which are more complicated and well established. Another noteworthy feature is that a manufacturing project such as procurement and capacity monitoring with regard to labor and machine deployment can be managed extremely well in the SAP project system environment.
A project system has a complicated and advanced group of features along with protracted and complex integration with other SAP elements to permit data access and management of a seamless nature. This offers considerable financial control aspects, user-level restrictions with regard to document access and other data, and protection within the firewall.
Learn SAP HANA from Industry Experts
Conclusion:
A good grasp of all the modules mentioned above will enable an individual to grasp how SAP is used to implement and enhance operations within an enterprise. As an SAP consultant, knowledge of these modules is critical to succeeding in a workplace that is run using SAP tools and processes.






 99999999 (Toll Free)
99999999 (Toll Free)  +91 9999999
+91 9999999