What is SAP FICO?
Category: SAP FICO Posted:Mar 13, 2019 By: Alvera Anto
SAP ERP is one of the powerful Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. SAP stands for System, Applications, and Products in data processing and it was developed by SAP AG, in Germany. SAP AG, founded in 1972 and released the SAP R/3 system product in 1992, which is a three-tier client/server technology. SAP provides the best solutions to all types of industries and service sectors. SAP has been providing developments in management across business and IT domain in different ways. It includes various integrated modules that cover almost all the features of business management. The different modules in SAP are SAP Sales and Distribution, SAP Material Management, SAP Production Planning, Quality Control, SAP FICO, etc. This article explains about SAP FICO and its various sub-modules.
SAP FICO is one of the essential functional modules in SAP ERP components which help the organization to manage all of its financial data. The primary purpose of SAP FICO is to support the organization to produce and handle all the financial statements for analysis and reporting and also assist with effective business planning and decision making. SAP FICO comprises of two modules, i.e., SAP Finance (FI) and SAP Controlling (CO), each of these modules are used to carry out specific financial processes. SAP FI module focuses on complete financial reporting and accounting while SAP CO emphasis on planning and monitoring costs. SAP FI and SAP CO were originally released as separate modules, but now these modules are integrated so strongly that most of the people are referring them as a single module.
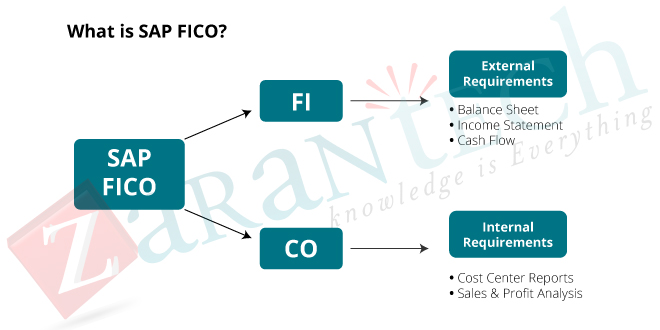
Now, let’s talk about SAP FICO and its submodules:
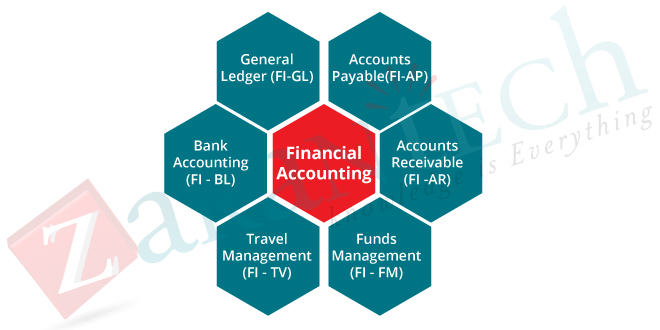
SAP FI module: SAP FI stands for Financial Accounting, and it is one of the essential modules of SAP ERP. It is used to store the financial data of an organization. SAP FI helps to analyze the financial conditions of a company in the market. It can integrate with other SAP modules like SAP SD, SAP PP, SAP MM, SAP SCM, etc.
SAP FI includes the following sub-components:
- Finance Accounting General Ledger.
- Finance Accounting Accounts Receivable and Payable.
- Finance Accounting Asset Accounting.
- Finance Accounting Bank Accounting.
- Finance Accounting Travel Management.
- Finance Accounting Fund Management.
- Finance Accounting Legal Consolidation
SAP FI module mainly deals with the following financial components:
- Fixed asset
- Accrual
- Cash journal
- Accounts receivable and payable
- Inventory
- Tax accounting
- General ledger
- Fast close functions
- Financial statements
- Parallel valuations
- Master data governance
Since the IT is enhancing in several sectors, companies have demanded more and efficient workforce, but financial accounting is the only department of any organization that seems to hold up if automation is utilized because even workforce also has its own limitations. Advanced features of SAP FI have made it among the most popular modules to be implemented in any organization. The tools and SAP FI suite comes in the strong union of a suite that aims to provide top quality service to any organization in an area of financial needs and accounting activities. Since the arrival of the internet, the importance of finance and its awareness has reached every corner of the world.
Now, let’s try to understand SAP FI Submodules in details:
General Ledger Accounting: A General Ledger contains all the transaction details of a company. It acts as the primary record to maintain all accounting details. Common general ledger entries are customer transactions, purchases from vendors, and internal company transactions.
Accounts Receivable: Account receivable module is responsible for capturing all transactions with customers and managing their accounts. In this module, separate customer accounts will be maintained, and when transactions are forwarded in customer’s accounts, the reconciliation accounts in the general ledger will get updated. Account receivables include various transactions such as invoice posting, credit memo posting, down payments, invoice payment, etc.
Accounts Payables: Account payables module is responsible for capturing all the transactions of vendors, and it also manages vendor accounts. Different vendor accounts are reserved and when transactions are sent in customer accounts, reconciliation accounts in general ledger get updated. Various transactions of account payables are invoice posting, credit memo, posting, down payments, invoice payment, automatic payment, etc.
Asset Accounting: Asset Accounting deals with all the fixed asset of the company and provides all the transaction details about fixed assets. The asset accounting module of Finance Accounting works closely with other modules like SAP MM, SAP Plant Management, EWM, etc.
Bank Accounting: It deals with all the transactions done through the bank. It includes all the incoming and outgoing transactions performed, balance management and bank transaction master data. You can create and process any bank transactions using the Bank accounting component.
Travel Management: This module is used to manage all the travel expenses of a company. It involves the entire travel request, their planning, and expenses involved in all the requested trips. It helps an organization to manage travel expenses efficiently, as it provides integration with all the other modules of SAP
Fund Management: This module is used to manage funds in a company. Fund Management module interacts with other modules like Bank accounting, General Ledger (G/L, SAP AR/AP, and SAP Material Management, etc. to get fund details. It involves all the transactions for fund receive, fund expenditure, and future expenses. It helps a company to create budget forecasting and to use the funds properly.
SAP Controlling (CO) is another important SAP module offered by an organization. It supports coordination, monitoring, and optimization of all the processes in an organization. SAP CO includes managing and configuring master data that covers cost and profit centres, internal orders, and other cost elements and functional areas.
SAP CO: This module supports in supervising, justifying, and planning business processes in every organization. CO module is directly related to financial accounting; it can be used as one view and organized the linked costs. It is also used to manage and configure master data which measures the information associated with the cost centres, internal orders, profit centres, cost elements and many more. The process is managed step by step including organizing, chasing, execution, and reporting. With the help of this module, we can trace cost heads to plan consequently. Based on activities, SAP CO module benefits the costing across processes. It manages product modifications, costs and it’s costing. It also involves constituents related to profitability analysis, Internal Order Accounting, Cost Centre Accounting, Overhead Management, etc. There are various components of SAP CO modules; let’s now discuss these modules in details:
- Cost Element Accounting − Cost and Revenue Element Accounting delivers you with an overview of the costs and revenues that occur in an organization. Most of the values are moved automatically from Financial Accounting to Controlling. Cost and Revenue Element Accounting only calculates costs, which either do not have another expense or only one expense in Financial Accounting.
- Cost Center Accounting − Cost Center Accounting is used for controlling purposes within your organization.
- Activity-Based-Accounting − It is used to analyze cross-departmental business processes.
- Internal Orders − Internal orders in SAP CO are used to collect and control, according to the job that incurred them. You can assign budgets for these jobs that are system monitored to ensure that they are not exceeded from the set budgets.
- Product Cost Controlling − It calculates the cost of manufacturing a product, or to provide a service. It allows you to calculate the price at which you can profitably market it.
- Profitability Analysis − It is used to analyze the profit or loss of an organization by individual market segments. Profitability Analysis provides a basis for decision making. For example, it is used to determine price, conditioning, customer, distribution channel, and market segment.
- Profit Center Accounting − It is used to evaluate profit or loss of individual, independent areas within an organization. These areas are responsible for their costs and revenues.
SAP CO Integration with Financial Accounting:
Both SAP CO and SAP FI modules are independent modules in an SAP system. The data flow between these components takes place regularly. Data flows applicable to cost flows to Controlling from Financial Accounting. At the same time, the system assigns the costs and revenues to different CO account assignment objects, such as cost centres, business processes, projects or orders.
Go through our Interview Questions SAP FICO to crack the Interviews
Conclusion
SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) is one of the modules which deal with finance-related roles. It is the most widely apprehended products in terms of scope and implementation. This shows that it is already used in many organizations and many of the enterprises are adopting it as their financial software platform.
Check out this insightful video on SAP FICO Tutorial for Beginners:
These are the related articles that you can check
- How SAP FICO Impacts the Growth of a Business
- SAP FICO: Is it Right for me?
- Importance of an SAP FICO Consultant in Finance Industry
- Career Opportunities for SAP FICO Certified Professionals
- C_TFIN52_67 SAP Certified Application Associate – Financial Accounting with SAP ERP 6.0 EhP7 – Certification Made Easy!!




 99999999 (Toll Free)
99999999 (Toll Free)  +91 9999999
+91 9999999