A Guide to SAP S/4HANA Deployment
Category: SAP S/4HANA Posted:Sep 11, 2020 By: Alvera Anto
It is becoming exceptionally difficult and intricate to choose the S/4 HANA tool deployment model and organizing alternatives. Currently, there are numerous options available in the market and each has its own advantage.
SAP S/4HANA is the digital core that empowers enterprise businesses to take advantage of all breakthrough technologies like in-memory systems, boosted user experience, streamlined IT landscape, Internet of Things (IoT), real-time analytics, mobility, big data, and many more next-generation technologies. Currently, SAP S/4HANA is available with 2 implementation options, cloud, and on-premise. SAP provides the cloud version while the on-premise version is available for either the consumer to host in its data center or on a partner cloud.
SAP S/4HANA Cloud – The below picture illustrates the SAP roadmap for the S/4HANA cloud, updated on a quarterly basis. This option offers benefits around scalability, management, and security that businesses need to outmatch competition in today’s fast-paced digital economy.
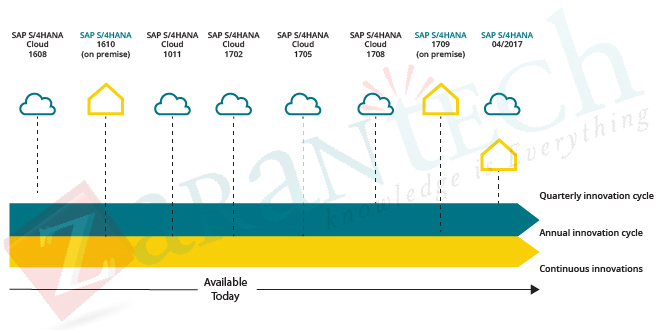
SAP S/4 HANA On-Premise – The image below represents the SAP roadmap for its on-premise version, with large annual updates, while regular FPS/SPS is launched for minor changes.
Hardware deployment for On-Premise version can be done through 2 ways, i.e. Appliance & TDI (customized Data Integration).
- SAP HANA Appliance – SAP HANA appliance is an “all-in-one-box” option, where all the required components are pre-build together and delivered as a solution from a particular hardware vendor. Currently, there are close to 13 hardware vendors who give licensed HANA appliances and consumers can choose to go with any of them depending on their overall software and hardware requirements.
- SAP HANA TDI Model– SAP HANA Tailored Data Integration allows the client to use their existing equipment and infrastructure resources, unlike appliance alternatives. TDI model also provides consumers with additional versatility and options with hardware infrastructure. Customers can choose their favoured infrastructure vendor and components from a set of licensed SAP HANA hardware(Storage space/ Calculate/ Network). The general hardware expense can be considerably minimized by using the existing available framework components, however facilities maintenance cost might increase as the overall responsibility of HANA facilities will be left with the customer or the infrastructure service provider(AMS vendor).
The on-premise S/4HANA application landscape can be released in an on-premise, public or private cloud hosting model.
- On-Premise Hosting Model (Device/ TDI) – The HANA appliances will be hosted on customers/partners existing data centre along with other SAP applications.
- Private Cloud (Appliance/ TDI) – HANA cloud infrastructure operated exclusively for a single organization, whether managed internally or by a third-party and hosted internally or externally. Consumers can bring their own SAP S/4HANA license (BYOL) or request strategic partners to handle that with an overall commercial proposition (Partner Managed Cloud).
- Public Cloud Microsoft (Like Azure/ AWS) – HANA cloud is called a ‘Public cloud’ when scalable and flexible IT-enabled capacities are offered as a service to customers using internet technologies. Presently Microsoft Azure provides 4TB as the largest S/4HANA appliance (available in the US) & AWS offers 2TB as its biggest appliance.
Conclusion
Want to figure out more about SAP S/4HANA Deployment, feel free to visit our website.
At ZaranTech, we also offer a self-paced, online certification program on SAP S/4HANA, mentored by some of the sought after and experienced subject matter experts. Browse through our course pages for further information.
Happy learning!





 99999999 (Toll Free)
99999999 (Toll Free)  +91 9999999
+91 9999999