Blockchain Technology-A Guide for Beginner’s
Category: Blockchain, ZaranTech Training Posted:Dec 14, 2018 By: Serena Josh
Blockchain technology is becoming very popular these days that everybody from a small shopkeeper to a stakeholder is curious to know about this innovative technology. Most of the people are eager to explore and capitalize on this field. The Blockchain is the primary support behind the bitcoin (a form of electronic cash). A bitcoin is a distributed digital currency that can be transferred between users on a peer-to-peer network without any mediator. Any transactions happen on the network are verified by network nodes using cryptography and recorded in a distributed public ledger called Blockchain. This article explains the fundamentals of Blockchain Technology.
Blockchain History: An anonymous person named Satoshi Nakamoto had published a white paper in the year 2008, which explained an innovative method of transferring money between two parties directly without any mediators. The name given to this idea was “Bitcoin”. Since Bitcoin uses the fundamental idea of cryptography; this new method of transferring money was characterized as crypto-currency. Bitcoin was developed with a single purpose of executing financial transactions, but later the investigators understood that its primary technology could be picked up to create other robust and secure applications that can transform the approach behind the working of existing systems. This foundational technology was named as Blockchain.
Why we need Blockchain Technology?
The current financial transactions system is not very well secured and effective. It has several transactional problems such as double spending, fraud, high transaction fees, financial crises, and crashes, etc. Let us understand these issues with the help of examples:
Double Spending: Suppose you want to transfer $1500 to your two friends, but you have only $1000 in your account. You have started the two transactions concurrently one of $1000 and other of $500. Usually, the transaction should not happen as there is insufficient balance in your account. But, the transaction can get completed by duplicating the digital token linked with every digital transaction without the required balance; this is called double spending. Thus, double spending is an error or attack where the single digital token is paid twice or more than one transaction.
High Transaction Fees: This is the most common problem which every customer is facing while making the transaction. Let us take an example to understand this issue; John has to transfer $1000 to his friend, but before it goes to the concerned person it should pass through a trusted third party such as a bank. Since this transaction bank is involved $2 is detracted from John’s account, and his friend will receive only $998. Similarly, there will be high transaction charges for the significant amount of transactions.
Frauds and Account Hacking: Well, the number of fraud and hacking cases associated with credit /debit cards and internet banking is increasing daily. The hackers or unauthorized person can use your user ID and password and make the transaction without your knowledge or consent.
These are some of the common issues which most of the people are facing today. Well, here comes the requirement of Blockchain which helps to resolve the above-listed problems. Let us now learn the Blockchain technology in detail.
Public Ledgers: Blockchain has a public ledger, i.e., the transactions happen on the Blockchain are open so that everybody connected with the system can access it. After joining the Blockchain network, you can download the entire list of all the transaction. In Blockchain, the details of the people who are involved in the transactions remain unknown, although the entire record is available publicly.
Decentralized System: Dissimilar to banks or other financial organizations which are controlled by central or Federal experts, the Blockchain technology follows a distributed method. Everyone in the system has equal responsibility for the enhancement and failure of the system, i.e., instead of one single authority holding power, each person involved with the system has some authority.
Verification of every single transaction: In Blockchain each transaction is confirmed by verifying the ledger and then sending the validation signal after a few minutes. Thus, the problem of double-spending is removed with the help of numerous complicated encryption and hashing algorithms.
No Transaction Fees: In Blockchain, the transactions fees usually are not relevant, but few alternatives of Blockchain implement certain minimal transactions fees. However, these transactional charges are relatively small as compared to the expenses inferred by banks and other financial firms. If there is a transaction which should be completed on priority basis, then the user should add extra transaction fees.
What is Blockchain and how it works?
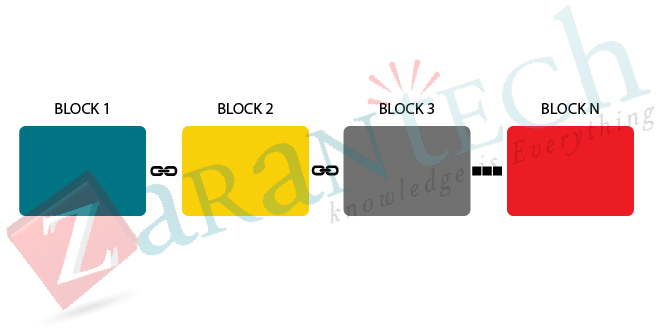
A Blockchain is a sequence of blocks which holds some useful information. The information which is stored inside a block depends on the type of Blockchain. The initial block in the series is referred to Genesis block. Each new block in the chain is connected to the previous block. With the help of Blockchain technology, the users not only carry out the transactions using crypto-currencies but also confirm the security and privacy of the clients involved in the transactions. A Blockchain can act as an open and distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties in a provable manner. This record is publically shared with everyone on the system which carries transparency and faith into the system.
A block in a Blockchain records all the recent transactions, and once it is done it goes into the Blockchain as a permanent database. After the completion of each block, a new block is generated. A Blockchain involves features such as SHA256 Hash Function, distributed Peer to Peer network, and Proof of Work.
All these features ensure the security of all the blocks present in a Blockchain. Let’s have a look at them.
SHA256 Hash Function: A block contains a Hash Function. The Hash Function is similar to a figure print and unique to each block. It is used to recognize a block and all of its contents. So whenever a block is created a hash function is assigned to it and if any block is modified its corresponding hash function will also get changed. Thus, hash function plays an integral part in finding the changes to the connections. Each block contains the data, hash function and a hash function of the previous block.
To understand the hash function let’s consider the below example.
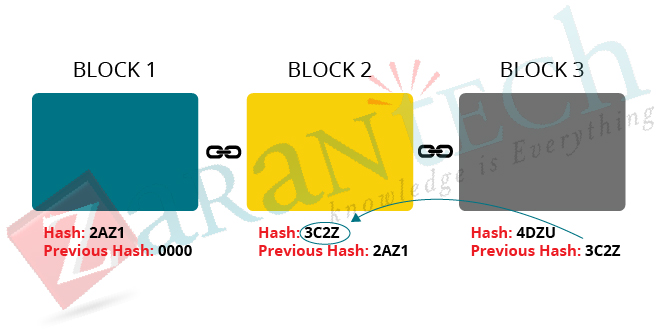
Here, there is a chain of 3 blocks. Since the first block has no predecessor, it does not have any hash function. The second block contains a hash function of the first block, and similarly, the third block includes the hash function of the second block. Due to this technique, the Blockchain becomes more secure.
So, if anyone wants to modify the data present in any block let say the second block, the corresponding hash function will also get updated. But, the third block still contains the old hash function of the second block; this makes the third block invalid. Similarly, all the following blocks become invalid, and hacker or attacker would not be able to modify the data in any block.
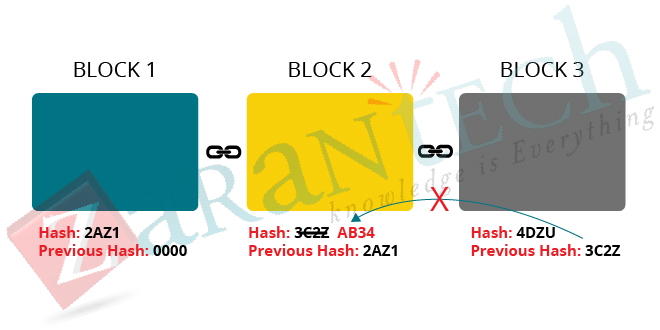
Proof of Work: Even though, the hash function is an excellent approach to the security of blocks. But, nowadays the computers are high-speed and can calculate numerous hash functions in a few minutes; this gives a chance to an attacker to modify a block and recalculate the hash functions of other succeeding blocks. Thus, in order to avoid this problem, Blockchain utilizes an idea called proof of work.
It is similar to solving a big riddle which needs a lot of computational effort. In the Bitcoin network, miners are responsible for performing the computational work. They verify the transactions and solve the complex mathematical riddle associated with each new block being created. It requires about 10 minutes calculating the necessary proof-of-work to add a new block to the chain.
Let’s consider the above example again; if the hacker wants to modify the data in the second block, he has to perform proof-of-work which may take about 10 minutes and then only can change the third block data and all the following blocks in the Blockchain. Thus, this approach takes much time and becomes very tough for the attackers to modify the blocks and hence make the Blockchain secure.
Peer-to-Peer Distributed Network: Blockchain utilizes a distributed peer-to-peer network, rather than using a central unit to manage the complete chain, and thus enables everyone to join the network. When anyone enters into this network, he or she will receive the entire copy of Blockchain. Each computer present in a network is referred as a node.
When any client creates a new block, this new block is sent to every client present on the network. Every node on the network has to verify the block to ensure that it has not been changed. After verifying the block, each node adds this block to their Blockchain.
All these nodes make a consensus and agree about which blocks are valid and which are not. The altered blocks are rejected in the network by all the nodes. So, to successfully alter with a Blockchain, it is required to modify all the blocks in the chain, recreate the proof-of-work for each block and take control of more than 50% of the network. Thus, any node will not accept the modified block on the network, and hence Blockchain becomes more secure.
Want to know More about Blockchain Training? Click here
Conclusion:
The Blockchain is a chain of blocks that hold useful information. It is the primary support behind the Bitcoin which is a distributed digital currency that can be transferred between two parties over a decentralized network without any intermediary. It is a secure method of performing various transactions. With the help of Blockchain technology, various transactional issues with the existing banking system such as high transactional fees, double spending, financial crises, fraud and account hacking are resolved.




 99999999 (Toll Free)
99999999 (Toll Free)  +91 9999999
+91 9999999