Why SAP MDG (Master Data Governance)?
Category: SAP MDG Posted:Feb 27, 2017 By: Ashley Morrison
SAP MDG (Master Data Governance) is an expected addition of the business approaches running in the SAP Business Collection, offering domain-specific MDG to centrally generate, modify as well as distribute Master Data. In this article, we are going to explore an overview of the SAP MDG and reasons on why it is being preferred.
Overview of SAP MDG
With SAP MDG, SAP presents a combined data management device for the validation, maintenance, and allocation of Master Data. SAP MDG is highly suitable for the SAP ERP system within the Business Suite of SAP. This combination stimulates the maintenance strategies, allows for a vast enhancement in the Master Data quality and guarantees the legal requirement observance. In addition, the automated workflow present in the SAP MDG enables the acceleration and stabilization of the business and maintenance processes.
Since MDG allows the Master Data volume up to one million records per object, organization experiences the raising size as well as internationalization. Hence, they can able to face the challenge of functioning an effective Master Data management unit. Reliable and accurate Master Data, establish the fundamentals for the entire business processes. Inconsistencies in customer’s addresses, payment terms or risk goods details can drive to notable delays in the business process. For example, incorrect deliveries, settlement of invoices, etc. In addition, the differences lead to complete shipments of goods not getting their appropriate destination. This situation not only leads vast Financial risk for the organizations but also raises the risk of having wrong business decisions because of inconsistent data.
Learn SAP MDG from Industry Experts
Organization’s complexity is replicated in its Master Data as well as its governance. The maintenance of the Master Data, primarily takes place in heterogeneous system settings at local and global levels. Master Data are generated as well as handled globally and improved with local characteristics. With SAP MDG, organizations can overcome these challenges and can control entire master processes automatically and uniformly. They can maintain Master Data accuracy and consistency across their enterprise by utilizing forceful data governance functions to maintain, create and duplicate Master Data. Consistent Master Data Governance supports the enterprise to better function key activities like new product introduction, Financial consolidation, and supplier onboarding.
Why SAP MDG?

With SAP MDG, the enterprise can enjoy following facilities:
- Centrally maintain supplier, Financial, material, customer and other data for steadiness across the enterprise
- Advantage from a provable audit trail signifying why, when and by whom data is changed
- Apply, integrate and reuse available business logic as well as infrastructure to authenticate data
- Use pre built User Interfaces and Workflows on verified data models
- Duplicate Master Data to non-SAP and SAP systems, by enabling maintenance and creation of a Master Data Governance
- SAP MDG allows the single solution, which can provision both central governance and consolidation shortens management and minimizes TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
- Offers single, trusted data view and address EIM (Enterprise Information Management) and MDM challenges.
SAP MDG Benefits
- It uses the typical SAP ERP checks
- Reuse discrete, existing SAP data structures and functionalities
- Adaptation and expandability to customer-specific needs
- UI is configurable, adaptable and customizable with the support of Floor plan manager
- Integrates rule-based workflow through BRFplus that can be adjusted individually and quickly. It also allows automated workflow control. For example, principle of simple double verification
- Consolidation and harmonization of the data in varied system
- Compliance with observance requirements
- Transparency on tasks in the field of Master Data handling
- Transparency on how the data affect business processes
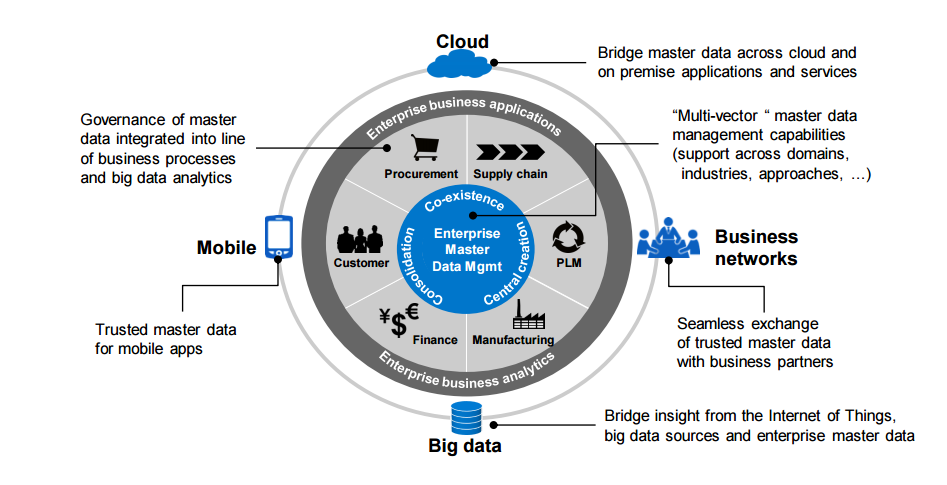
The following figure demonstrates the advantages of MDG:

MDG across Lines of Business

Because accurate and complete Master Data is the primary requirement for agility and competitive functions across entire lines of business, tapping entire applicable stakeholders in the seat of the driver is vital. This means merging them flawlessly into the maintenance of data workflow, which is depending on the tasks according to full process transparency, domain expertise and usage of business rules.
Master Data serve as the enterprise DNA and it enables several evolving strategies.
The following figure shows the impacts and key trends of SAP MDG in business and technology:
Img Source: support.sap
Challenges in Financial Accounting
If the Financial Master Data is distributed inconsistently across the organization, a large amount of manual effort is required to update the Master Data in the Financial systems. This situation not only raises the noncompliance risk with the IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) and the SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley) act but also reduces the speed of group classes.
CFO’s are searching answers for the following question:
- How can we accelerate the Financial close via harmonized data across various systems?
- How can we minimize manual work during updating Financial Master Data?
- How to enhance the quality of data in the multisystem environment?
- How can we safely and efficiently execute as well as track needed changes?
Challenges in Supply Chain & Procurement
When it comes to the Supply Chain, the absences of visibility into materials and suppliers influences the overall performance of a company.
Key Decision makers are searching answers for the following questions:
- How can we correct as well as finish supplier data that in turn support to enhance Financial welfares (for instance, conditions, discounts as well as central contracts)?
- How can we get an exact view of suppliers and supplies (for instance, detect duplicate, evaluate performance and analyze expense) to enhance procurement decisions?
- How can we announce new products faster?
Challenges In Customer Relations
When it comes to customer relations, uneven data satisfies entire customer-facing transactions. The marketing or sales head of organizations searching answers for the following questions:
- How can we support to make sure that the order-to-cash processes aren’t troublesome?
- How can we make marketing campaigns more efficient?
Innovation of MDG

When it comes to managing the difficulties of Master Data handling whilst optimizing the SAP investment. SAP MDG provides several benefits.
The application offers pre configured data models, validations, role-based User Interfaces and predefined workflows.
The workflow can be enhanced with minimum effort, facilitating several people to append their expertise in the handling of complex Master Data. For instance, one employee can make changes in the classification details in a substantial master, and another employee can append alternative measurement units and their conversions.
The workflows contain steps for endorsement of the modified data. Until endorsement, the data exist in a staging region, which is discrete from the product Master Data. Once they are approved, the data is dispatched to the creative Master Data tables. The data then distributed to the entire system, which subscribes to the modification of these Master Data. By this way, MDG delivers consistent authorization, definition, and duplication of data to SAP Business Systems and non-SAP systems.
By tracking all these approvals and changes, MDG facilities a complete and compliance audit trail. MDG also offers flexibility to outspread the delivered copies or to create entire new MDG applications depending on the Custom-Defined data models along with suitable roles, workflows, validations and User Interfaces.
C_MDG_90 – SAP MDG Interview questions
MDG Support For Financial Data
- Support Finance enterprises accelerate Financial close
- Facilitates companies to centrally build Financial data objects as well as spread these objects to decentralized units
- This supports to guarantee the standard usage of entities acts entire Financial units, including Reporting, Operational, Financial and Planning Consolidation units
- Offers a collective setting in which Financial specialist can argue new objects, avoid making unwanted objects, and attain the entire audit track for entire changes
- Accounts for time needs for data modification and group’s alteration request
MDG Support For Supplier Data MDG
- Facilitates companies to coordinate and control the difficult process of building and apprising supplier data
- The process needs various people with various specializations to contribute at the exact time and in the exact order to guarantee timely accuracy and obtainability of the details
- Includes a flexible rule-based platform for data authentication to support guarantee the data quality in the making process
- Supports to remove data redundancy via duplicate identification and integration functions
MDG Support for Material Data
- Arranges the Data Maintenance process across various users, supporting to make sure that the data is consistent, complete and accurate in the view of creation
- Enhances the reliability of material and product Master Data across the complete Business network
- Documents modification along the entire lifecycle of the materials to support guarantee compliance
MDG Support For Customer Data
- Enables organizations to gain a richer, deeper understanding of the customer based, up-to-date and non-redundant information
- Supports to rationalize entire customer-based business transactions including sales, marketing, and service
- Supports to enhance profits and revenue and enables cross-sales chances
How MDG Authorizes Business With Authenticated Data?
The SAP MDG application offers the customer a robust Master Data established for enhanced process Flexibility, Business Efficiency, and Simplified. The current version of MDG extends the consolidation functionality of Master Data to the domain of material data in addition to customer data and supplier. New integration approaches enable a switching of data across the Ariba supplier & performance management solution, SAP S/4 HANA and Hybrid e-commerce solutions by supporting customers to manage data across on-premise and hybrid cloud processes and applications in a better way.
How SAP MDG Enhances Quality and Data Management?
SAP MDG provides a wide range of features for handling Master Data assets as well as associated data policies and terms from a central location. MDG is a repository-based data governance device that is specially designed to support a company’s Master Data quality as well as data policy management requirements. Companies can manage and identify key data assets utilizing personalized glossary terms and metadata, determine data rules and policies, easily trace the lineage of their data and define data ownership.
How SAP MDG Differs From MDM?
MDM (Master Data Management) is a term, which includes several different meanings based on the maturity of the Master Data organization of the company and the technologies, which are utilized to facilitate Master Data.
The main reason that SAP has defocused stating MDM technology is that they have resigned themselves to the option, that they will never be a huge performer in the MDM space, which they believed they could be. MDM is just strongest with reporting analytics and ERP. This is possible due to the technology was misaligned with available SAP solutions and it was excessively ambitious for the requirements and points of several clients who were struggling with quality and consistency problem with Master Data, but could not obtain their heads around requiring to invest in an entirely new solution.
On the other hand, when it comes on MDG, it is about syndicating fundamental attributes of the data to diverse and peripheral systems of records (such as CRM and ERP) and focused on nourishing the data engine of SAP application.
Both SAP MDG and SAP MDM provide similar abilities; however, targets at various objectives. MDG is targeted openly for the governance of Master Data and includes restricted data integration abilities. MDM is targeted clearly at strong data integration and data distribution across various systems, both non-SAP and SAP systems. It has some essential data governance abilities.
Both MDG and MDM can be utilized in the same companies with one performing as the Master Data distribution and management integration and another one decently for Master Data Governance.
This leads ERP to focus more on Master Data; however, it does not force the technology adoption, which really includes a very restricted implicit value for everyday operations as if MDM. Customer acknowledges the existence of bad data but does not essentially subscribe to the idea, which it is as universally damaging as MDM users suggest.
SAP MDG is a different contribution, formed using available technology stacks and effortlessly merged into the bequest platform of the SAP ERP; however, does not essentially invert the available entry, data collection and maintenance methods.
In the end, the SAP MDG solution for SAP application data is something that every customer could think as a better strategy than the swamp standard SAP ERP.
Advantages of SAP MDG?
The MDG platform is adaptable for the organization of all sizes. With the Data Management and Data Governance features in a single product, SAP MDG allows companies to control their data-oriented tasks without the requirement for multiple frameworks. This supports minimize confusion about data internal management and asset location practices. MDG can also combine with other available SAP platforms.
For questions or added info on this subject, you can visit our website. At ZaranTech we offer self-paced online training programs on SAP MDG topics. Enroll with us and skyrocket your career.
Check out this insightful video on SAP MDG Tutorial for Beginners:
Learn SAP MDG and Get Certified
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes




 99999999 (Toll Free)
99999999 (Toll Free)  +91 9999999
+91 9999999